Nonpartisan Electoral Advocacy
Advocacy is an umbrella term that encompasses the efforts individuals or organizations make to identify, embrace, and promote causes. Nonpartisan electoral advocacy consists of the advocacy efforts made during an election year that are not aimed at a single candidate or party, but rather at getting an organization’s stakeholders — like employees, association members, or the public — to participate in the election, including registering to vote. Lobbying is a focused form of advocacy that constitutes an attempt to influence specific legislation. Although lobbying is considered a form of advocacy, lobbying efforts must be recorded and reported as addressed by state and federal law through the IRS.
Examples of nonpartisan electoral advocacy efforts include:
- Voter education/Assisting voters in understanding the election process
- Distributing nonpartisan questionnaires to voters
- Engaging the general public in the electoral process
- Sponsoring nonpartisan candidate forums or debates
- Distributing nonpartisan materials regarding all candidates
- Organizing voter registration campaigns
Why is Nonpartisan Electoral Advocacy Important?
Electoral advocacy ensures that engagement in the election process is high so that voters, future decision makers, and current decision makers are educated on the causes that matter most to your organization. It’s vital for voters to understand the electoral process, know when elections are taking place, and who the candidates are. Voters pay the most attention to public policy issues and causes during the run-up to elections as they are actively mentioned by candidates. This provides an opportunity for organizations to guide candidates and organizations to focus on the issues that are relevant and most important to their organizations.
The Association of Equipment Manufacturers’ (AEM) advocacy strategy provides a great example of how organizations can combine electoral advocacy and issue advocacy in one campaign action center to drive increased engagement across both efforts:
In early 2020, AEM wanted to engage member companies in their grassroots advocacy and Get Out the Vote (GOTV) efforts. Their efforts were intended as a means to educate people in the industry about the issues that mattered to the equipment manufacturing industry while building excitement about grassroots advocacy and recruiting new advocates. To do this, they built an advocacy website that included several actions ranging from registering to vote to watching videos to learn about key policy initiatives. They used gamification (where advocates could earn points when they took action) to encourage advocates to participate in both electoral advocacy and issue advocacy efforts.
Nonpartisan electoral advocacy urges stakeholders to be involved and informed on the electoral process. Both electoral and grassroots advocacy attempt to engage the general public to take action in the political processes —nonpartisan electoral advocacy through the electoral process, grassroots advocacy the regulatory and legislative processes. With the right outreach and engagement strategies, you can support both.
Nonpartisan Electoral Advocacy vs. Lobbying
Contrary to grassroots advocacy—when an organization informs and encourages stakeholders to take action (like writing to or calling their legislators) on the issues that matter the most to the company—direct lobbying refers to an organization’s attempt to influence specific legislation through the disclosure of their stance to a legislator, their staffers, or any government official that has a direct influence on the production and regulation of legislation.
Advocacy is an umbrella term for promoting causes through different means, like emailing Congress, calling state legislators, or using social media to promote a stance. As previously mentioned, electoral advocacy refers to the advocacy efforts that take place during an election year that do not support or oppose a single candidate or party.
Lobbying, or legislative lobbying, is a form of advocacy that is specifically focused on influencing legislation in one direction. Lobbyists attempt to sway legislation in their favor to promote their organization, association, or group interests. Lobbying and advocacy are often used interchangeably; however, since lobbying efforts are strictly regulated by the IRS, specifically defining lobbying activities is essential.
Electoral Advocacy Do’s & Don’ts for 501(c)(3) Organizations
Election years provide great opportunities for 501(c)(3) organizations—public nonprofits or private foundations—to promote participation in civic society and gain new advocates during a time when substantially more attention is paid to public policy. However, despite the opportunity election years present for swaying legislation in an organization’s favor, there are strict regulations that prevent 501(c)(3) organizations from supporting or opposing specific candidates for office, and thus, remaining nonpartisan is of utter importance. The IRS strictly regulates 501(c)(3) advocacy activities as detailed in the following table:
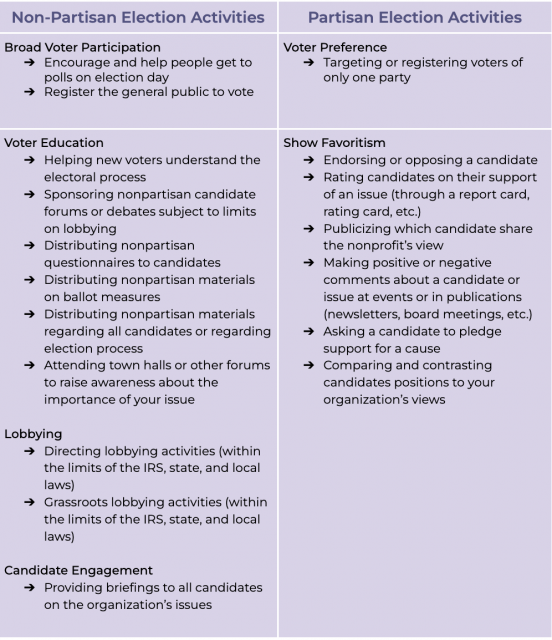
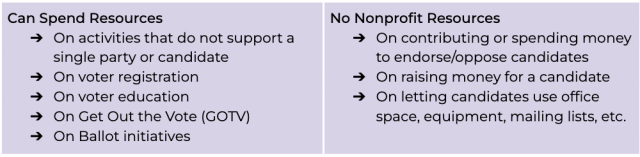
Additionally, resources from 501(c)(3) organizations should only be put towards nonpartisan efforts as outlined below:
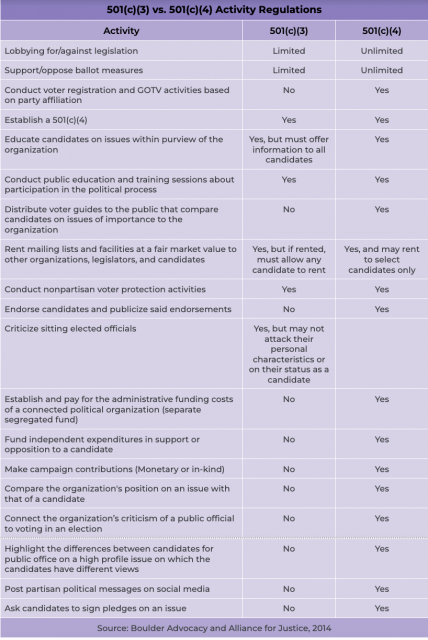
501(c)(3) vs. 501(c)(4) Organizations
501(c)(3) organizations can work with other coalitions, including Political Action Committees, and other groups that participate in partisan activities so long as the coalition is not engaged in partisan campaign activities. If the partner coalition becomes involved in partisan campaign politics, the organization should remove itself as a supporter of the coalition in all regards and any funds contributed by the organization cannot be used as a means to support any one candidate by the coalition.
Compared to 501(c)(3) organizations, 501(c)(4) organizations—tax-exempt social welfare organizations— have different advocacy regulations; therefore, when partnering with 501(c)(4) organizations knowledge of the difference in regulation is crucial.
Conclusion
When combined with grassroots advocacy and legislative lobbying, electoral advocacy can round out your engagement strategy with stakeholders by getting them involved in your organization’s key issues. Especially as policymaking winds down leading up to an election (as politicians focus on fundraising and voter engagement), electoral advocacy gives your team a chance to keep advocates engaged while your other campaigns may be on pause.